Life Extension Magazine®
Summary: Atherosclerosis and heart health
Dr. Joel Kahn, MD, shares his experience on how two plant extracts, French maritime pine bark and Centella asiatica, can help slow the progression of atherosclerotic plaque and even help reverse atherosclerosis.
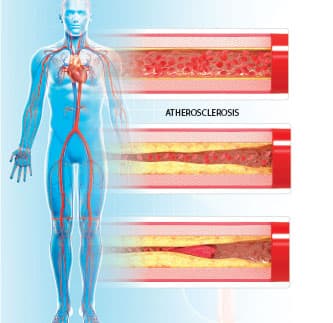
I have devoted my career as a cardiologist to finding ways to treat atherosclerosis—the buildup of plaque in artery walls.
I’ve relied primarily on healthy lifestyle changes, diet, and supplements.
A few years ago, a human study found that a combination of two plant extracts significantly reduced arterial plaque in the carotid arteries when added to diet, exercise, and healthy lifestyle counselling.1
I have recommended these plant extracts to thousands of patients and have seen the favorable results firsthand.
Larger studies provide new evidence that arterial calcification and blockages are reversible.
My Clinical Practice
I spent seven years after medical school completing my training in interventional cardiology or using catheters to treat heart disease.
Much of my practice involved inserting stents to prop open coronary arteries that were occluded with atherosclerotic plaque.
But three weeks into my first job, I decided there was a better, more comprehensive approach.
At that time, I read a study in a respected medical journal focusing on atherosclerosis, which often leads to heart attacks and strokes.
The study reported that atherosclerosis had been reversed using lifestyle and diet changes.2
Since then, I’ve combined interventional cardiology with a search for lifestyle and supplement-based methods to stabilize and reverse plaque buildup.
I was particularly impressed by a published study that reported on a combination of extracts of French maritime pine bark and an herbal extract called Centella asiatica.
When added to standard diet, exercise, and lifestyle counselling, these two plant extracts improved plaque stability and reduced size and numbers of arterial plaques.1
The study involved 50 patients with plaque in the carotid arteries, which supply blood to the brain, neck, and face. These patients had no history of cardiovascular events, and did not have diabetes or metabolic problems. 1
Over the three-month study period, pine bark + Centella asiatica extracts reduced carotid artery plaque and lowered the number of plaques compared to a control group.
After these scientific findings were published, this pine bark-Centella extract combination became a routine part of my atherosclerosis reversal program.
The Evidence Mounts
I grew more convinced of the effectiveness of this plant combination when a larger, longer-term study was published in 2017.3
This time, 391 subjects were followed for four years.
All had asymptomatic atherosclerosis of either the carotid artery or the femoral artery (which provides blood to the leg). Atherosclerotic lesions extended 50%-60% into the arteries in at least one location.
Three treatment groups were formed. One was treated with extract of pine bark alone, another was treated with pine bark and Centella asiatica, and a third control group received no extracts. All groups received standard diet, exercise, and lifestyle counselling.
The rate of plaque progression, measured by ultrasound, was significantly lower in both treatment groups than in the control group. The group that took the combination of the two extracts had the greatest reduction in progression of plaque thickness and length.
The extracts also had a favorable impact on cardiovascular outcomes as follows:
- The occurrence of angina, chest pain caused by reduced blood flow to the heart, was less than 3% in the two extract groups, compared with 6.25% in control patients.
- The rate of heart attacks was significantly lower for the combination therapy.
- Events requiring hospital admission occurred in 16.4% of control subjects, 8.9% of subjects using only French maritime pine bark extract, and just 3.3% of patients using the combination of pine bark and Centella extracts.
Pine Bark - Centella Extracts in Practice
I have used this combination with countless patients in my clinic who have plaques clogging their carotid arteries.
I use the carotid intima-media thickness (ultrasound) test to identify and track carotid plaque status.
This test measures the thickness of the inner layers of the carotid artery, the intima and the media.4
Increased plaque means greater thickness, enabling this carotid ultrasound test to reveal atherosclerosis even in people with no symptoms.
I routinely observe reversal of plaque in patients taking the pine bark + Centella extract combination. I have even seen arterial age drop 10 to 20 years after only one or two years of therapy.
Preventing Arterial Plaque Progression
My use of these extracts has recently expanded again, based on data published in 2020.
This Italian trial involved 84 normal weight to mildly overweight subjects with asymptomatic atherosclerosis in their carotid and femoral arteries, determined by high-resolution ultrasound.
These atherosclerotic subjects were treated with similar interventions as the studies already discussed. The duration of this trial was three years.5
Patients with an atherosclerotic plaque that was blocking less than 50% of an artery and those with an atherosclerotic plaque blocking more than 50% of an artery were included in this trial.
All patients were given diet, exercise, and lifestyle counselling.
One group received no additional treatment, a second took 100 mg a day of aspirin, and a third received the aspirin plus the combination of extracts of French maritime pine bark (150 mg/day) and Centella asiatica (450 mg/day).
At the end of the three years, more than 20% of patients in the standard management and the aspirin group had progressed to more severe and extensive atherosclerotic plaque.
Among patients treated with aspirin + pine bark + Centella, only 5.3% of patients experienced plaque progression.
In the diet, exercise, and lifestyle-counselling group, 22% suffered a cardiovascular event requiring hospitalization. That number declined to 12% in the aspirin group and to just 3.5% in the group taking aspirin plus the two plant extracts.
What you need to know
Reducing and Reversing Plaque Progression
- Atherosclerosis is the buildup of plaque in artery walls.
- A combination of two plant extracts significantly reduced arterial plaque in the carotid arteries.
- French maritime pine bark-Centella asiatica extracts prevent plaque progression.
- This combination of plant extracts may reverse the progression of atherosclerosis.
Oxidative stress, a driver of atherosclerosis, was measured in the blood of all subjects and was lower in the group taking the pine bark and Centella extracts. This makes sense since both these plant nutrients are free-radical scavengers.
Decrease of Coronary Artery Calcification
The same research team evaluated the efficacy of the pine bark-Centella combination in asymptomatic atherosclerotic patients with coronary artery calcifications.6
Patients with atherosclerosis in the coronary arteries —those that supply the heart with blood—can experience angina, shortness of breath, and even a heart attack.7
The study included three groups of 30 men each with asymptomatic coronary artery calcifications. Although they didn’t have angina or shortness of breath, the calcification in their arteries indicated progressive atherosclerosis.
All subjects received standard diet, exercise, and lifestyle counselling and took 100 mg/day of aspirin.
The first group received no additional treatment. The second added 150 mg/day of French maritime pine bark extract. The third used the combination of 150 mg/day pine bark and 450 mg/day of Centella asiatica extracts.
After one year, there was a 35% increase in the number of coronary artery calcifications in the group that received diet, lifestyle, and exercise counselling plus aspirin. In those also taking pine bark alone, new calcifications were halted.
In those using the pine bark + Centella there was a significant 10% decrease in the number of calcifications, a remarkable result.
Testing in Patients with Stents
To evaluate the impact of pine bark and Centella asiatica extracts on atherosclerotic plaque progression in stented arteries, 160 stented patients with partial arterial blockage due to atherosclerotic changes (as determined by ultrasound) were grouped into one of three treatment arms.8
The study began 6-10 months after successful stent procedures, and patients were followed for 12 months.
All groups received diet, exercise, and lifestyle advice along with anti-platelet medication and low-dose statin. A second group received, in addition, the pine bark extract; and a third group received extracts of pine bark and Centella.
After 12 months, progression of atherosclerotic lesions on inner artery walls occurred in 6.7 times more patients in the diet, exercise, lifestyle, and medication-only group compared to the group that also received the combined pine bark + Centella extracts.
In fact, in just one year, nearly 60% of patients in the group that did not receive the plant extracts had marked progression of their atherosclerosis.
By contrast, among subjects who received the additional pine bark extract without Centella, only 18.5% experienced atherosclerosis progression.
Most remarkable of all, though, were the results in the pine bark + Centella extracts group. Just 8.9% of these patients had progression of atherosclerotic plaques.
In both groups that received extracts, there was a significant reduction in oxidative stress. No side effects or tolerability problems were observed with the plant extracts.
Summary
These studies consistently show that the combination of French maritime pine bark and Centella asiatica extracts slows and may reverse the progression of atherosclerosis.
The published findings reveal significant reductions in adverse cardiovascular outcomes.
I’ve observed these powerful results in my clinic as well.
The combination of these plant extracts (pine bark + Centella) has promise for millions of people with atherosclerosis.
If you have any questions on the scientific content of this article, please call a Life Extension® Wellness Specialist at 1-866-864-3027.
Joel Kahn, MD, is the founder of the Kahn Center for Cardiac Longevity in Bingham Farms, Michigan.
Conclusion: Lifestyle and atherosclerosis
There are several risk factors, such as age and family history, poor daily habits, and diabetes and obesity, that can contribute to atherosclerosis and cardiovascular diseases. As Dr. Kahn explains, making lifestyle changes can support overall cardiovascular health. Incorporating French maritime pine bark and Centella asiatica extracts into your wellness routine can help stabilize atherosclerotic plaque and protect against atherosclerosis.
References
- Luzzi R, Belcaro G, Ippolito E. Carotid plaque stabilization induced by the supplement association Pycnogenol(R) and centella asiatica (Centellicum(R)). Minerva Cardioangiol. 2016 Dec;64(6):603-9.
- Ornish D, Brown SE, Scherwitz LW, et al. Can lifestyle changes reverse coronary heart disease? The Lifestyle Heart Trial. Lancet. 1990 Jul 21;336(8708):129-33.
- Belcaro G, Dugall M, Ippolito E, et al. Pycnogenol(R) and Centella asiatica to prevent asymptomatic atherosclerosis progression in clinical events. Minerva Cardioangiol. 2017 Feb;65(1):24-31.
- Bots ML, Evans GW, Tegeler CH, et al. Carotid Intima-media Thickness Measurements: Relations with Atherosclerosis, Risk of Cardiovascular Disease and Application in Randomized Controlled Trials. Chin Med J (Engl). 2016 Jan 20;129(2):215-26.
- Belcaro G, Cesarone MR, Scipione C, et al. Delayed progression of atherosclerosis and cardiovascular events in asymptomatic patients with atherosclerotic plaques: 3-year prevention with the supplementation with Pycnogenol(R)+Centellicum(R). Minerva Cardioangiol. 2020 Feb;68(1):15-21.
- Hu S, Belcaro G, Cesarone MR, et al. Central cardiovascular calcifications: supplementation with Pycnogenol(R) and Centellicum(R): variations over 12 months. Minerva Cardioangiol. 2020 Feb;68(1):22-6.
- Available at: https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/coronary-artery-disease/symptoms-causes/syc-20350613. Accessed July 15, 2020.
- Belcaro G, Cesarone MR, Scipione C, et al. Pycnogenol(R)+ Centellicum(R), post-stent evaluation: prevention of neointima and plaque re-growth. Minerva Cardioangiol. 2019 Dec;67(6):450-5.

